What is finite element analysis
Finite element analysis (FEA) is the process of predicting an object’s behavior based on calculations made with the finite element method (FEM). While FEM is a mathematical technique, FEA is the interpretation of the results FEM provides. FEA gives engineers insights into complex systems and structures, helping them make more informed design decisions.
FEM uses math to break complex systems into smaller, simpler pieces, or “elements.” It then applies differential equations to each element individually, using the power of computers to divide, then conquer engineering problems.
FEA is the application of FEM equations and is the basis of many types of simulation software. It’s used to validate and test designs safely, quickly, and economically by creating virtual models of real-world assets.
Finite element modeling makes it possible to simulate the physical world without the expense, time, or risk of building physical prototypes. These models are used to solve for various conditions and scenarios across a variety of industries, especially those with complex or high-risk environments such as aerospace and biomechanics.
What are the Advantages of FEA?
Engineers face huge challenges in designing solutions that meet the evolving needs of people and planet. To explore unlimited scenarios and conditions, they rely on the flexibility of FEA. With FEA, it’s possible to model any shape geometry (from a square block to the human heart), at any size (from the nanoscale to a large passenger jet airplane ), with any type of physics (heat transfer, fluid dynamics, structural mechanics, etc.). Basically, as long as you have a partial differential equation, you can use FEA.
FEA advantages include:
Assess complex geometries: FEA can analyze intricate structures that would otherwise be challenging or impossible to evaluate.
Simulate a range of physics: FEA allows engineers to model multiple physics problems all at once.
Save time, money and resources: FEA reduces the need for physical prototyping so engineers can evaluate the safety, reliability and performance of a design before it’s ever built.
JST’s Finite Element Analysis Examples
Static structural analysis
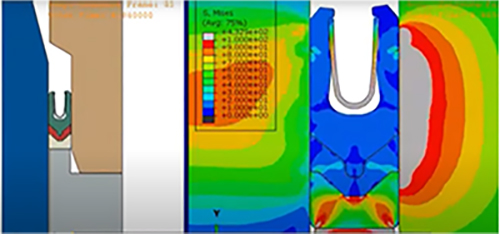
Analyze the relationship between product temperature and mold temperature & time; Provide suggestions for vulcanization process.
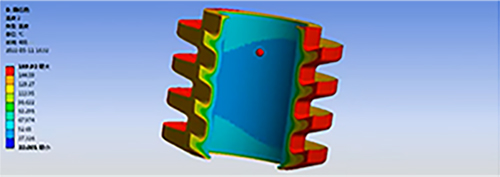
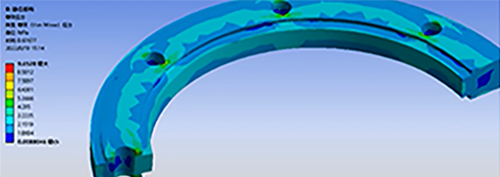
Analyze the rubber part of the product, Compression stiffness and stress analysis

New Blog
© Copyright: 2026 Guangzhou JST Seals Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Friendly Links:
VonesealsScan to wechat
